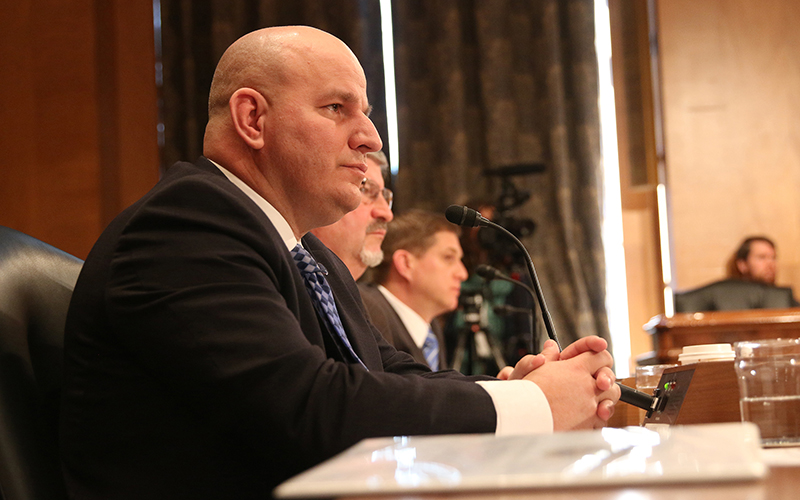

From left, National Border Patrol Council President Brandon Judd, National Treasury Employees Union President Anthony Reardon and National Immigration and Customs Enforcement Council President Chris Crane testify to the Senate committee. (Photo by Andres Guerra Luz/Cronkite News)
Sen. Ron Johnson, R-Wisconsin, and Sen. Claire McCaskill, D-Missouri, listen to testimony from labor union officials who said plans to hire thousands of new border and immigration agents could be thwarted by outdated hiring processes. (Photo by Andres Guerra Luz/Cronkite News)
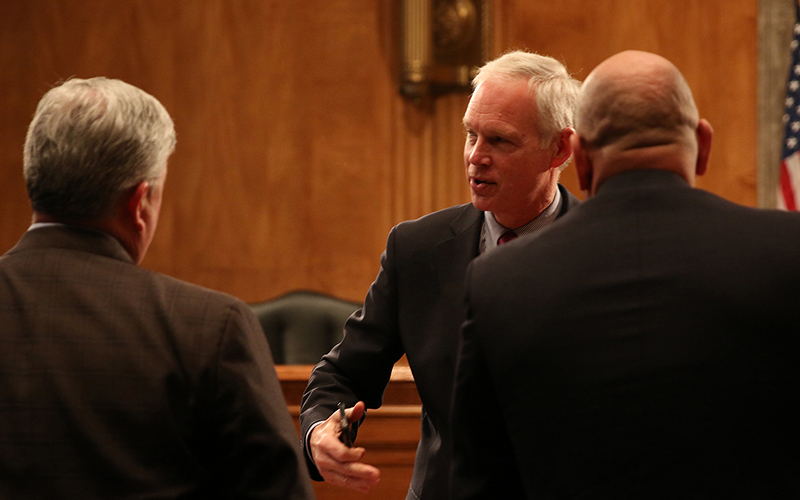

Sen. Ron Johnson, R-Wisconsin, speaks with union officials Anthony Reardon, left, and Brandon Judd after a Senate committee hearing during which they questioned the government’s ability to quickly hire thousands of border and immigration officers. (Photo by Andres Guerra Luz/Cronkite News)
WASHINGTON – A Trump administration plan to hire thousands more border and immigration officers is “desperately” needed, but unlikely to happen quickly at agencies plagued by low morale and a cumbersome hiring process, witnesses told a Senate panel Wednesday.
Labor union leaders for Customs and Border Protection and Immigration and Customs Enforcement testified that CBP has yet to fill the 2,000 jobs Congress authorized in 2014. At the same time, low morale has led to a situation where “we’re losing more agents than we can hire,” said Brandon Judd, the president of the National Border Patrol Council.
“Although the news of hiring new agents and infrastructure is welcome, we have to take a realistic approach in understanding the hiring and retention challenges Border Patrol has faced over the last 20 years,” Judd said in testimony prepared for the hearing by the Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs.
The hearing was called to look at the current ability of the Department of Homeland Security agencies to hire 15,000 more agents – 5,000 CBP officers that President Donald Trump called for in one of his first executive orders and 10,000 ICE agents that Secretary John Kelly identified in a directive.
The only witnesses at the hearing were representatives for border and immigration agents. Sen. Claire McCaskill, D-Missouri, said in her opening statement that she asked Homeland Security “to send anyone – anyone! – to testify at today’s hearing and DHS has failed to provide a single representative.”
The CBP said in an email after the hearing that it will be able to meet “critical hiring needs” by recruiting people who have already been vetted by the government – military and law enforcement officials, for example. The statement said the agency plans to maintain agency standards by giving applicants polygraph examinations.
But witnesses at the hearing said current administration of polygraph tests is just one of the bureaucratic problems plaguing the agencies. Border Patrol does not administer polygraphs correctly, they charged, failing three times more people than other federal agencies and turning away 70 percent of its applicants.
Hiring efforts are also hindered by unattractive work situations that drive off current workers and discourage potential applicants, they said. Those problems include a lack of accountability for supervisors that created “overheavy” and “overbearing” management at a time when the agencies need more officers in the field, critics said.
National Treasury Employees Union President Anthony Reardon said that border agents are often forced to work long hours with little public gratitude, making it hard to keep and attract agents. He told the committee that some border agents are given “involuntary temporary duty assignments” that entail 16 hour shifts for days in a row, at locations far from home.
-Cronkite News video by Ziyi Zeng
Some have told him that they start falling asleep on their drives back home, he said.
“That’s just wrong to do to human beings,” Reardon said.
Judd told the committee in a written statement that the agency only hired 485 agents last year – a pace at which the agency would take more than 10 years to meet the administration’s hiring demand.
Witnesses said additional agents are needed to enforce security at ports of entry, prevent drugs from coming across the border and deport violent immigrants who are here illegally.
Some committee members cited a recent Maryland case in which a 14-year-old schoolgirl was raped by two undocumented immigrant teens, while others pointed to cases in which previously detained immigrants were released and then killed or assaulted a U.S. citizen.
Judd said if border enforcement agencies had been more effective, the deaths and assaults of those U.S. citizens would not have happened.
“We failed the citizens of this great nation by not securing the border,” Judd said.
The Border Patrol only arrests half the people who cross the border illegally, Judd said, adding that a portion of those arrested get released.
McCaskill said she supported the hiring – which she said was more often requested by agents she met with than a border wall – but asked how Homeland Security agencies will be able to hire thousands more employees if they can’t even keep staff levels at the current hiring cap.
She called border security a bipartisan issue. She and the committee chairman, Sen. Ron Johnson, R-Wisconsin, often agreed during the meeting in calls for immediate action on reforming agency hiring processes and management.
“All of us want to secure the border, the question is not whether or not we want to secure the border,” McCaskill said. “The question is what is the right strategy to really get at this problem?”